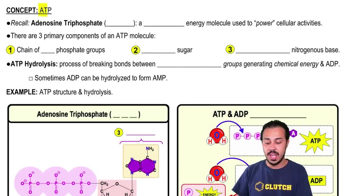
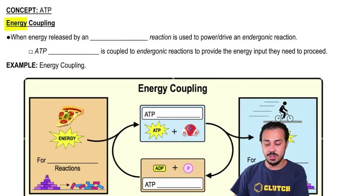
Multiple Choice
When 1 mole of ATP is hydrolyzed in a test tube without an enzyme, about twice as much heat is given off as when 1 mole of ATP is hydrolyzed in a cell. Which of the following best explains these observations?
2065
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: