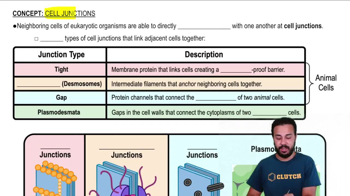
Textbook Question
Mark the following statements about the plasma membrane as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
Membrane cholesterol is vital for cell-cell recognition.
410
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 6:49m
6:49mMaster Biological Membranes with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning