Textbook Question
Identify and shade in the locations of all the ascending sensory tracts in the following diagram of the spinal cord.
486
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: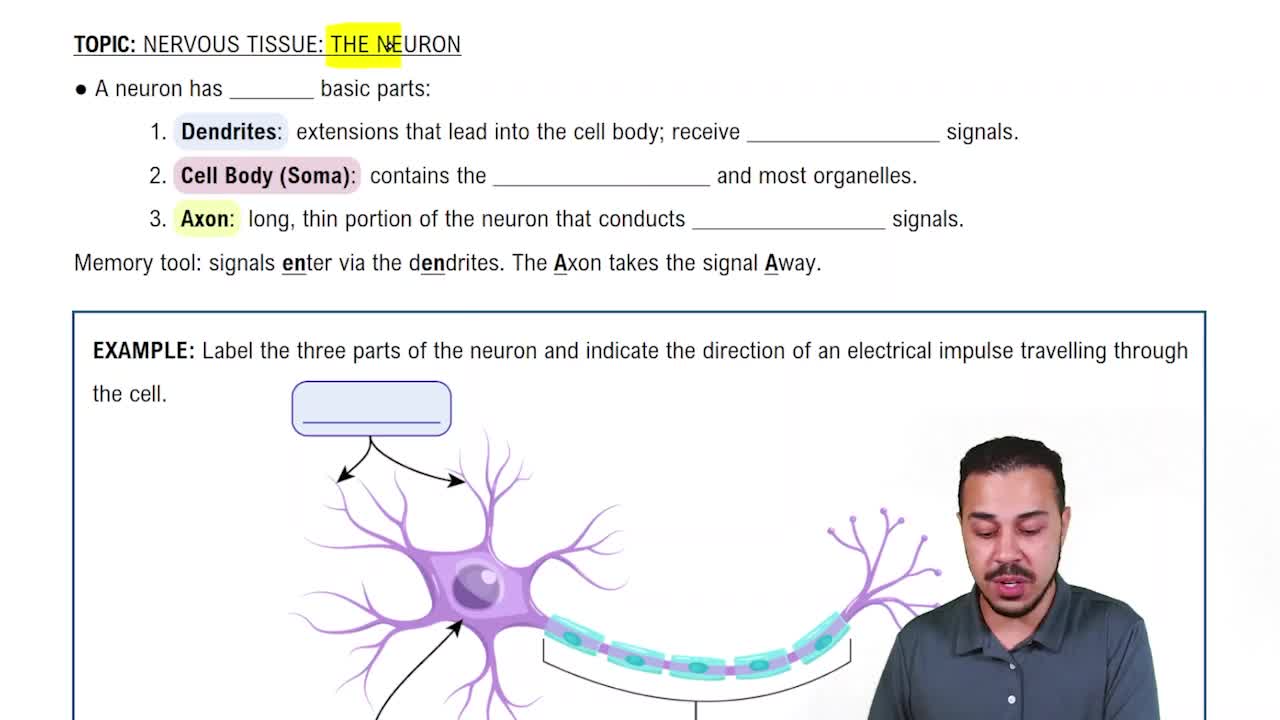



 1:32m
1:32mMaster The Central Nervous System with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning