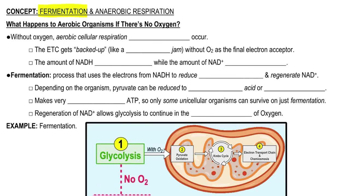
Characteristics of isometric contractions include all but:
a. Shortening
b. Increased muscle tension throughout the contraction phase
c. Absence of shortening
d. Used in resistance training
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: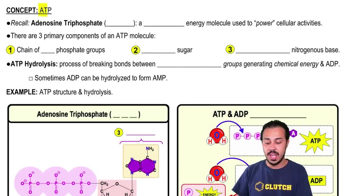


 4:53m
4:53mMaster Overview of Muscle Contraction with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning