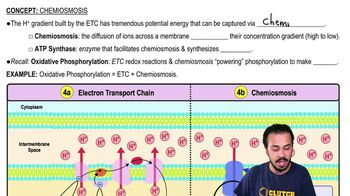
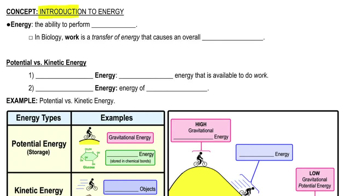
Textbook Question
What does the chemiosmotic hypothesis claim?a. ATP is generated using phosphates taken from intermediates in the electron transport chain.b. ATP is generated using a phosphate gradient produced by glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.c. ATP is generated using a proton-motive force that is produced by the electron transport chain.d. Water is generated using electrons taken from NADH and FADH2 and transported through the electron transport chain.
1700
views