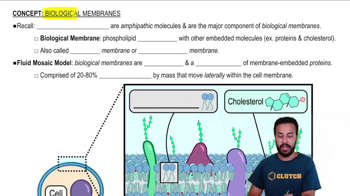
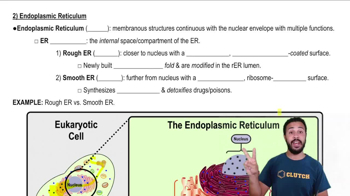
Textbook Question
Which structure is part of the endomembrane system?(A) mitochondrion(B) Golgi apparatus(C) chloroplast(D) centrosome
2417
views
1
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: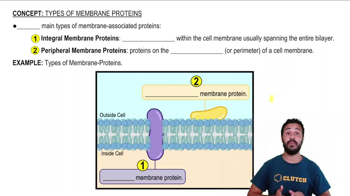

 4:13m
4:13mMaster Endomembrane System: Protein Secretion with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning