The description 'Articular surfaces deep and secure; capsule heavily reinforced by ligaments and muscle tendons; extremely stable joint' best describes
a. The elbow joint
b. The hip joint
c. The knee joint
d. The shoulder joint
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: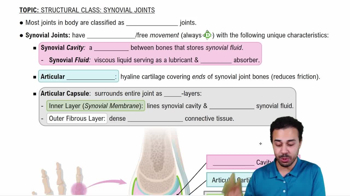


 1:19m
1:19mMaster Introduction to Classification of Joints with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning