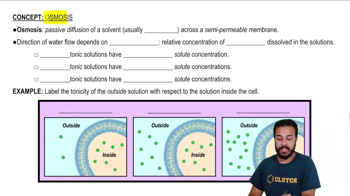
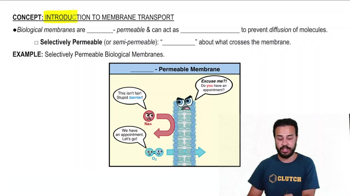
Multiple Choice
Seawater is hypertonic to cytoplasm in vertebrate cells and in plant cells. If a red blood cell and a plant cell were placed in seawater, what would happen to the two types of cells?
3429
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: