Multiple Choice
Cataracts are caused by changes to the crystallin proteins in the eye. Based on this information, what structure would you expect to be directly affected by cataracts?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
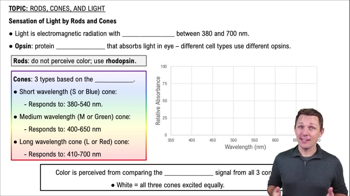
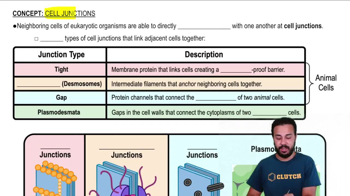

 5:4m
5:4mMaster Optic Components with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning