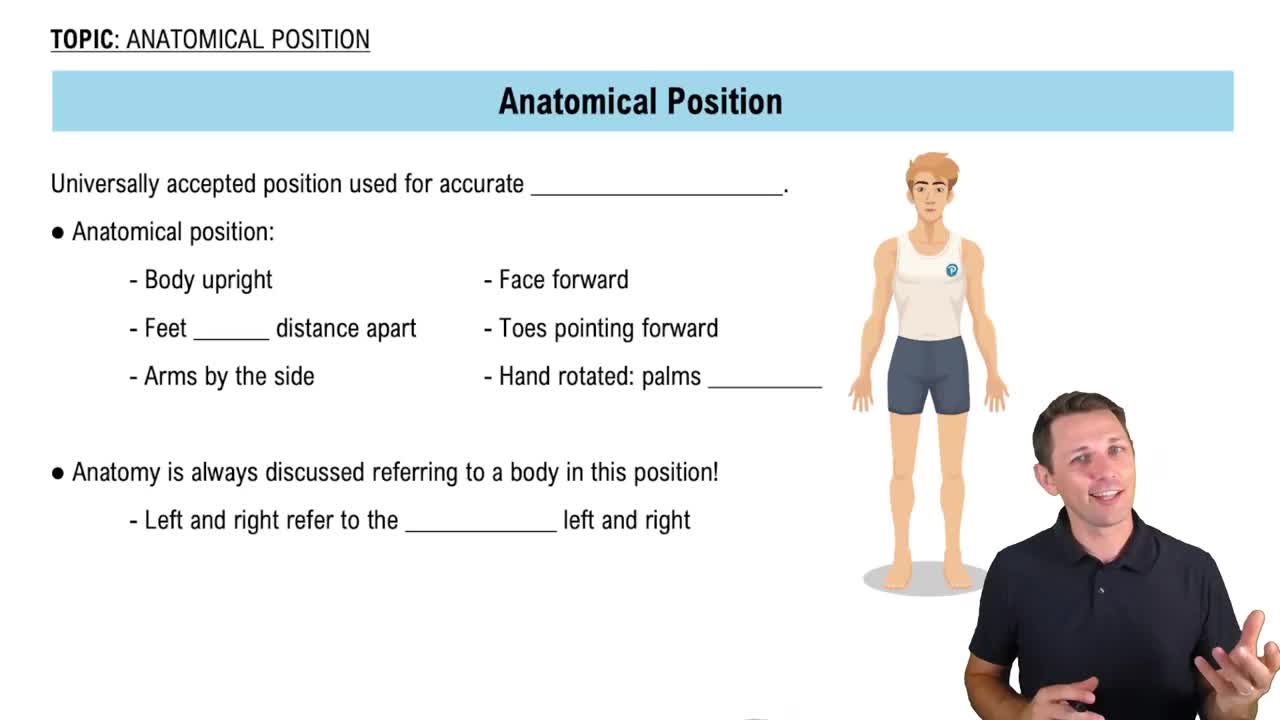
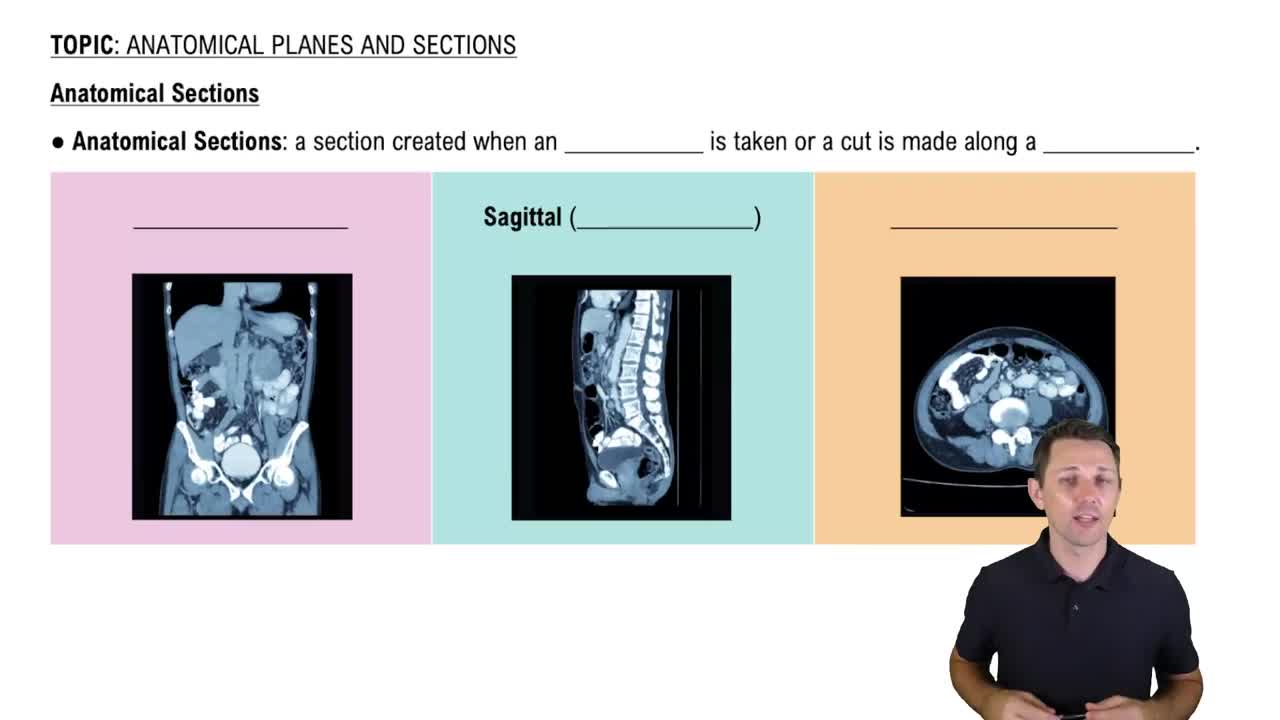
Multiple Choice
Which organ systems directly allow waste materials to be passed out of the body?
2841
views
41
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:29m
2:29mMaster Introduction to Organ Systems with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning