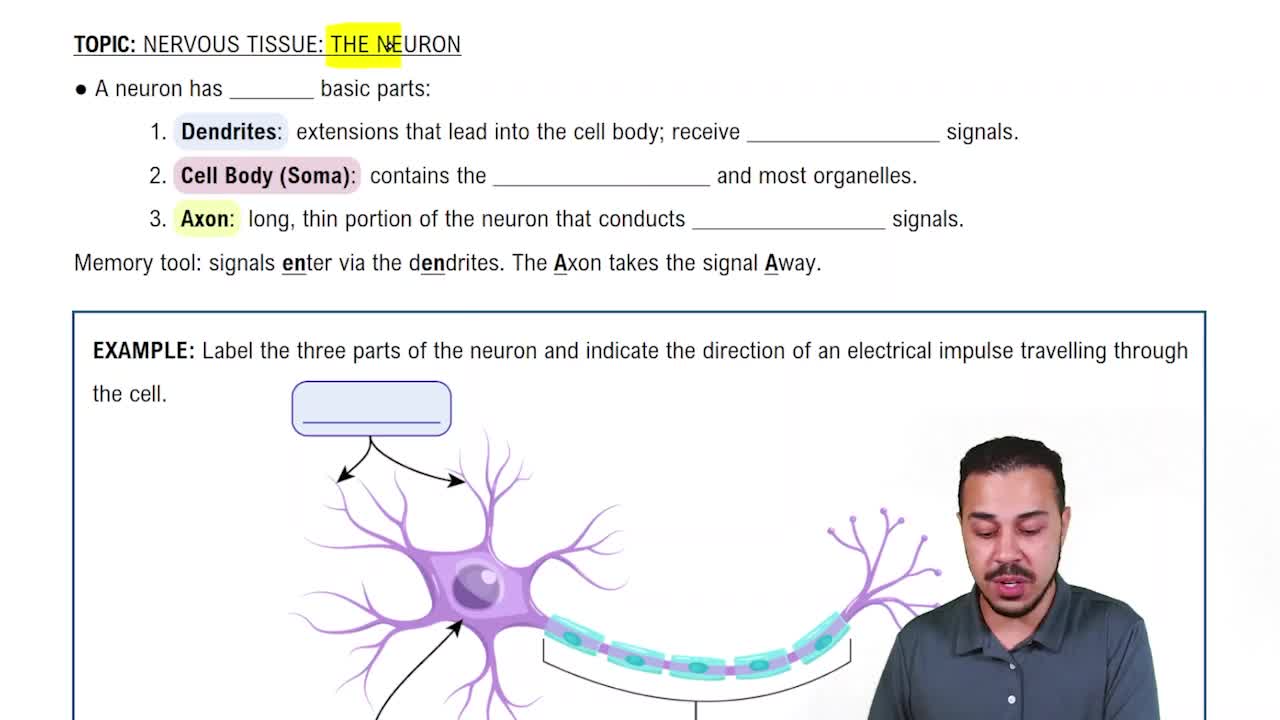
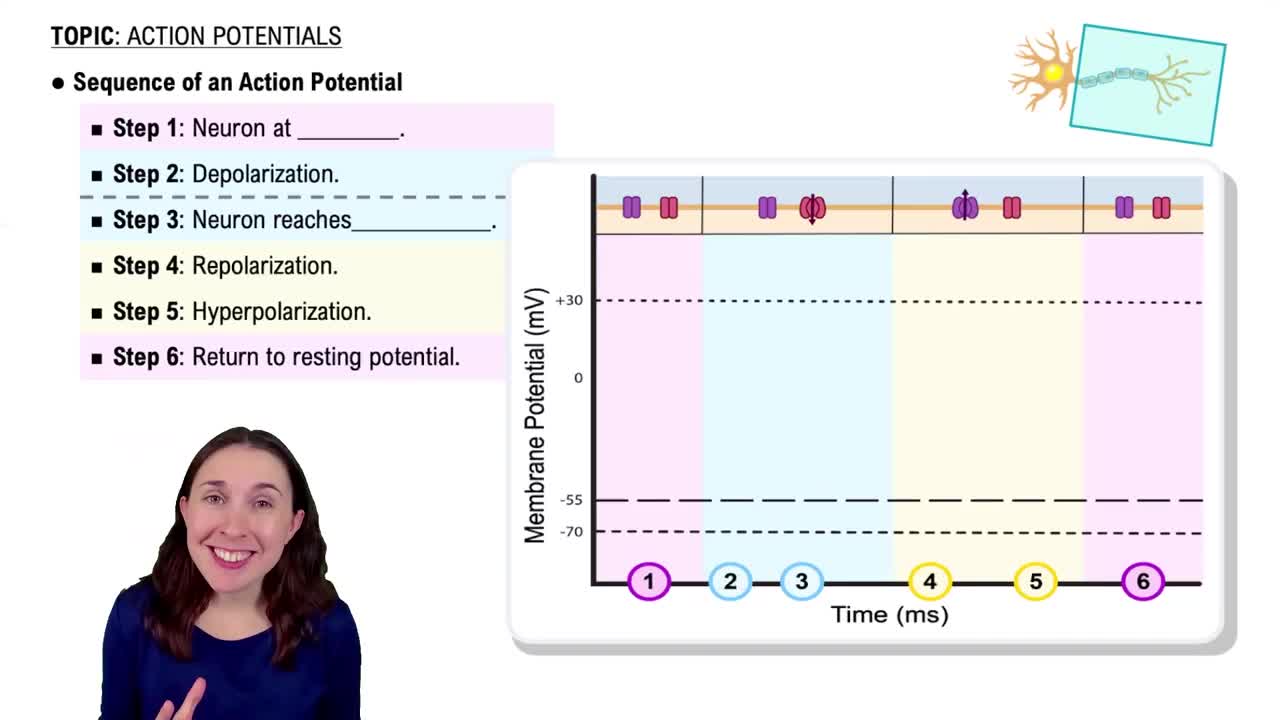
Which of the following cranial nerves is not involved in the gustatory sense?
a. Vagus nerve (X)
b. Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
c. Facial nerve (VII)
d. Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: