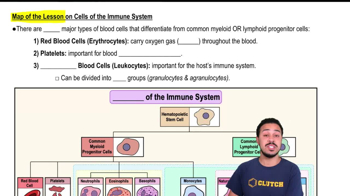
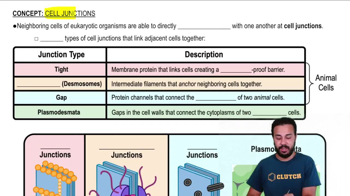
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct is to make a true statement.
In the primary immune response, the lag phase lasts about 5 days, during which time B cells proliferate and differentiate.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: