Multiple Choice
Which of the following groups is primarily involved in synthesizing molecules needed by the cell?
2279
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance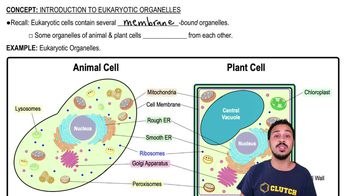
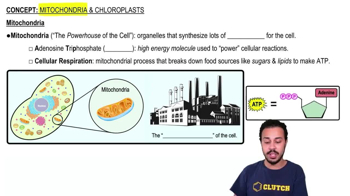


 3:45m
3:45mMaster Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning