Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells, the components of the electron transport chain are located in or on __________.
1654
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

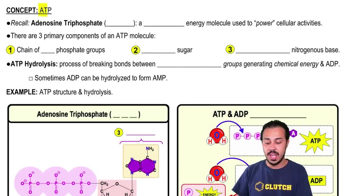

 7:41m
7:41mMaster Electron Transport Chain with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning