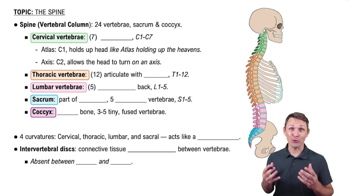
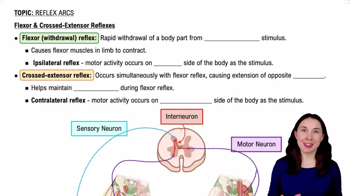
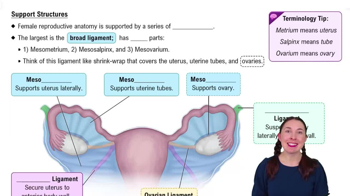
Name two muscles in each of the following compartments or regions:
f. Third muscle layer of the foot
g. Posterior compartment of leg
h. Medial compartment of thigh
i. Posterior compartment of thigh
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: