Multiple Choice
Transitional epithelium can be found in which body system?
2136
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: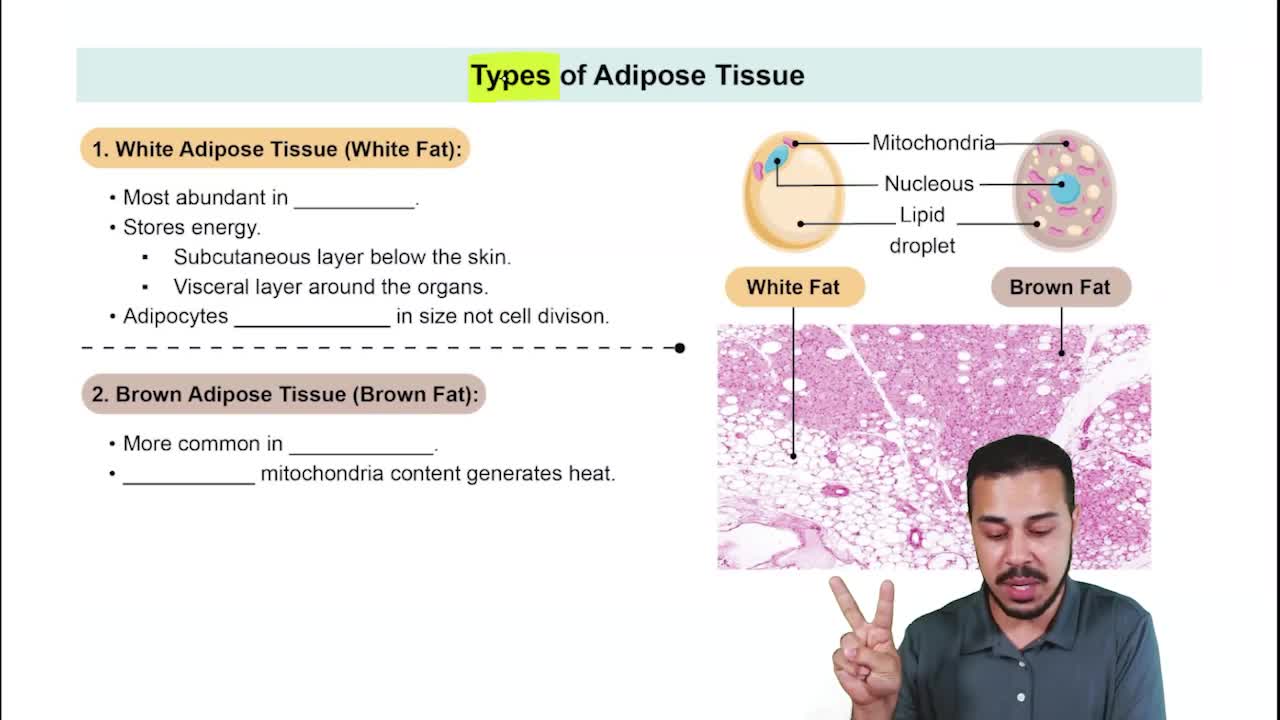
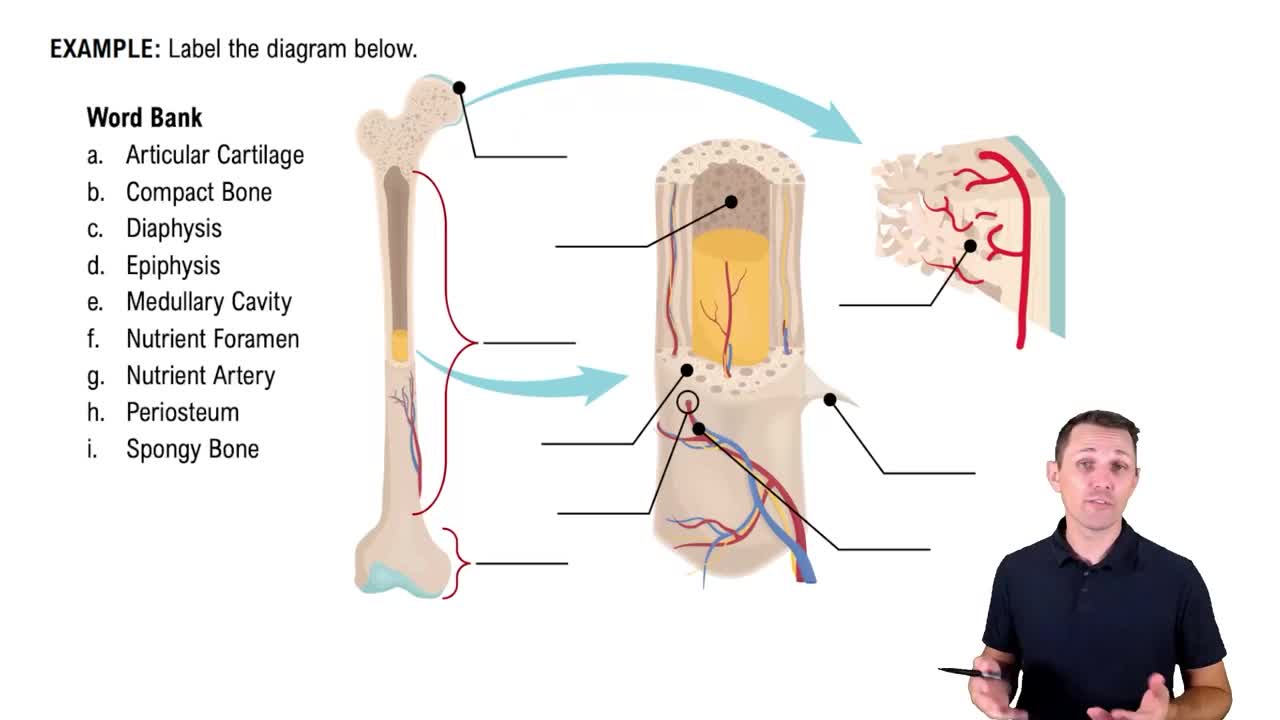
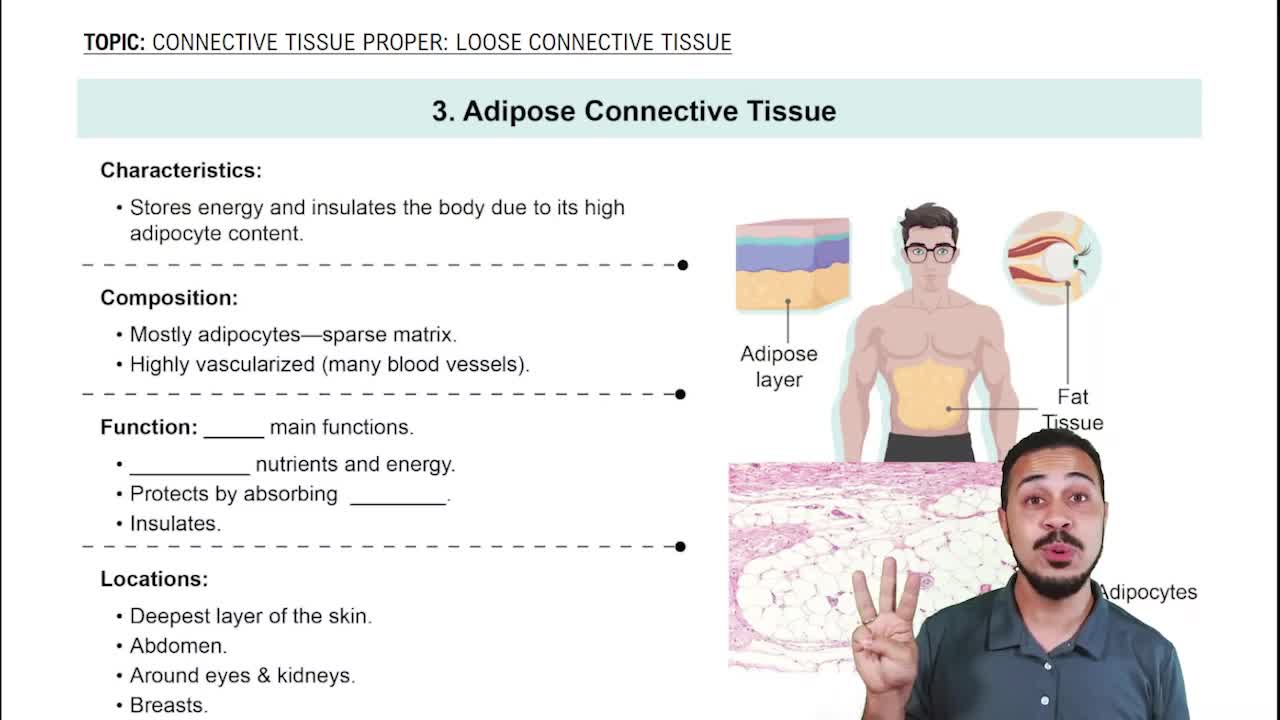

 3:40m
3:40mMaster Intro to Epithelia with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning