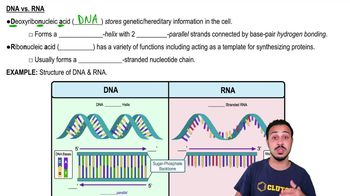
Textbook Question
The nucleotide shown here is called cordycepin triphosphate. It is a natural product of a fungus that is used in traditional medicines. If cordycepin triphosphate is added to a cell-free transcription reaction, the nucleotide is added onto the growing RNA chain but then no more nucleotides can be added. Examine the structure of cordycepin and explain why it ends transcription.
1112
views