Textbook Question
List the structural features in a prokaryotic cell.
2448
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: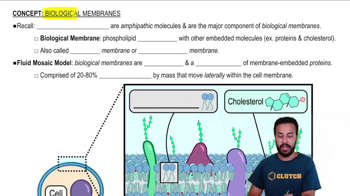
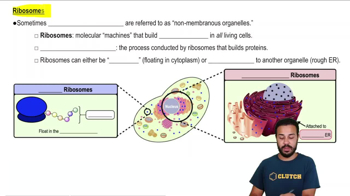


 5:54m
5:54mMaster Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning