Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Symbiosis
Symbiosis refers to a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms. It can be mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic, where both, one, or neither organism benefits, respectively. Understanding symbiosis is crucial to differentiate roles that involve direct interactions between organisms.
Recommended video:
Decomposer
Decomposers are organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that break down dead or decaying organisms, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. This role typically does not involve symbiosis, as decomposers act independently to process organic matter, unlike symbiotic relationships that require interaction with living hosts.
Recommended video:
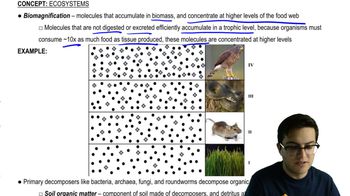
Biomagnification and Decomposers
Pathogen
Pathogens are organisms that cause disease in their host, often through parasitic relationships. While pathogens can be considered a form of symbiosis due to their interaction with hosts, they differ from mutualistic or commensalistic relationships as they harm the host, highlighting the diverse nature of symbiotic interactions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:57m
2:57m