Textbook Question
Label the parts of the following diagram illustrating the catalytic cycle of an enzyme.
2866
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
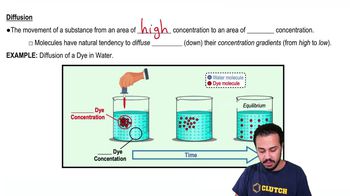

Label the parts of the following diagram illustrating the catalytic cycle of an enzyme.
Which best describes the structure of a cell membrane?
a. Proteins between two bilayers of phospholipids
b. Proteins embedded in a bilayer of phospholipids
c. A bilayer of protein coating a layer of phospholipids
d. Cholesterol embedded in a bilayer of phospholipids
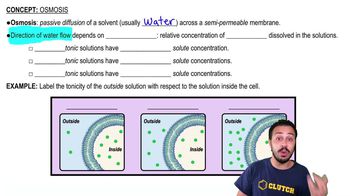
A plant cell placed in distilled water will ______________; an animal cell placed in distilled water will ______________.
a. Burst … burst
b. Become flaccid … shrivel
c. Become turgid … be normal in shape
d. Become turgid … burst