Foreign molecules that elicit an immune response are called
a. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
b. Antibodies.
c. Histamines.
d. Antigens.


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

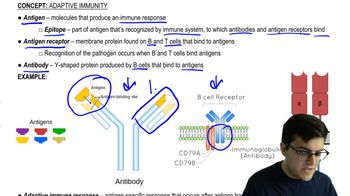

Foreign molecules that elicit an immune response are called
a. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
b. Antibodies.
c. Histamines.
d. Antigens.
Which of the following is not part of the vertebrate innate immunity defense?
a. Macrophages
b. Antibodies
c. Complement system
d. Inflammation
Which of the following best describes the difference in the way B cells and cytotoxic T cells deal with invaders?
a. B cells confer active immunity; T cells confer passive immunity.
b. B cells send out antibodies to attack; certain T cells can do the attacking themselves.
c. T cells handle the primary immune response; B cells handle the secondary response.
d. B cells are responsible for the cell-mediated immune response; T cells are responsible for the humoral immune response.