Textbook Question
Which of the following respiratory systems is not closely associated with a blood supply?
a. The lungs of a vertebrate
b. The gills of a fish
c. The tracheal system of an insect
d. The skin of an earthworm
1444
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


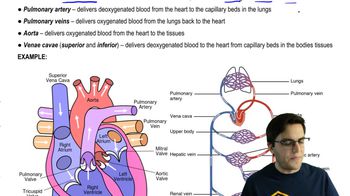
Which of the following respiratory systems is not closely associated with a blood supply?
a. The lungs of a vertebrate
b. The gills of a fish
c. The tracheal system of an insect
d. The skin of an earthworm
Pulse is a direct measure of
a. Blood pressure.
b. Stroke volume.
c. Cardiac output.
d. Heart rate.
When you hold your breath, which of the following blood gas changes first leads to the urge to breathe?
a. Rising O2
b. Falling O2
c. Rising CO2
d. Falling CO2
One feature that amphibians and humans have in common is
a. The number of heart chambers.
b. A complete separation of circuits for circulation.
c. The number of circuits for circulation.
d. A low blood pressure in the systemic circuit.