Textbook Question
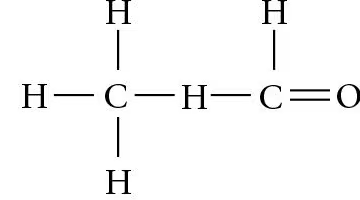
Identify the asymmetric carbon in this molecule:
2184
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Identify the asymmetric carbon in this molecule:
Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
a. The replacement of the —OH of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
b. The addition of a thiol to a hydroxyl
c. The addition of a hydroxyl to a phosphate
d. The replacement of the nitrogen of an amine with oxygen
Which of the molecules shown in question 5 has an asymmetric carbon? Which carbon is asymmetric?