Cooking oil lipids consist of long, unsaturated hydrocarbon chains. Would you expect these molecules to form membranes spontaneously? Why or why not? Describe, on a molecular level, how you would expect these lipids to behave in water.

Suppose a cell is placed in a solution with a high concentration of potassium and no sodium. How would the cellular sodium–potassium pump function in this environment?
a. It would stop moving ions across the membrane.
b. It would continue using ATP to pump sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
c. It would move sodium and potassium ions across the membrane, but no ATP would be used.
d. It would reverse the direction of sodium and potassium ions to move them against their gradients.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Sodium-Potassium Pump
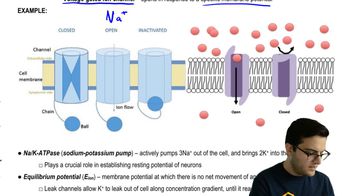
Concentration Gradient

ATP Utilization in Active Transport

Draw and label the plasma membrane of a cell that is placed in a solution with concentrations of calcium ions and lactose that are greater than those on the inside of the cell. Use arrows to show the relevant gradients and the activity of the following membrane proteins:
(1) A pump that exports protons
(2) A calcium channel
(3) A lactose carrier
In terms of structure, how do channel proteins differ from carrier proteins?
In an experiment, you create two groups of liposomes in a solution containing 0.1 M NaCl—one made from red blood cell membranes and the other from frog egg cell membranes. When the liposomes are placed in water, those with red blood cell membranes burst more rapidly than those made from egg membranes. What could explain these results? Select True or False for each of the following statements.
a. T/F The red blood cell liposomes are more hypertonic relative to water than the frog egg liposomes.
b. T/F The red blood cell liposomes are more hypotonic relative to water than the frog egg liposomes.
c. T/F The red blood cell liposomes contain more aquaporins than the frog egg liposomes.
d. T/F The frog egg liposomes contain ion channels, which are not present in the red blood cell liposomes.
Examine the experimental chamber in Figure 6.8a. Explain what would occur by osmosis if you added a 1-M solution of sodium chloride on the left side and an equal volume of a 1.5 M solution of potassium ions on the right. How might the addition of the CFTR protein to the lipid bilayer impact the direction of water movement?
