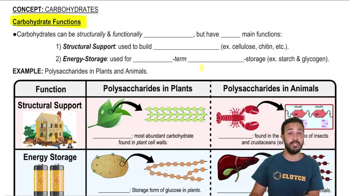
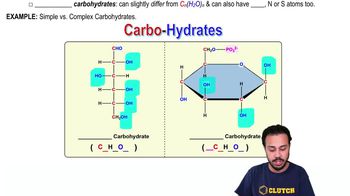
A glucose molecule is to starch as (Explain your answer.)
a. A steroid is to a lipid
b. A protein is to an amino acid
c. A nucleic acid is to a polypeptide
d. A nucleotide is to a nucleic acid
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: