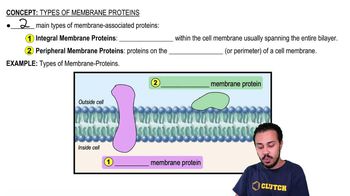
According to the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure, proteins of the membrane are mostly
a. Spread in a continuous layer over the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane.
b. Confined to the hydrophobic interior of the membrane.
c. Embedded in a lipid bilayer.
d. Randomly oriented in the membrane, with no fixed inside-outside polarity.