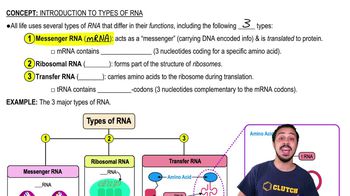
Progression through the cell cycle is regulated by oscillations in the concentration of which type of molecule?
a. p53, Rb, and other tumor suppressors
b. Receptor tyrosine kinases
c. Cyclins
d. Cyclin-dependent kinases
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: