Why is it important that the small intestine has a much greater surface area than the stomach or esophagus?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Biology2h 42m
- 2. Chemistry3h 40m
- 3. Water1h 26m
- 4. Biomolecules2h 23m
- 5. Cell Components2h 26m
- 6. The Membrane2h 31m
- 7. Energy and Metabolism2h 0m
- 8. Respiration2h 40m
- 9. Photosynthesis2h 49m
- 10. Cell Signaling59m
- 11. Cell Division2h 47m
- 12. Meiosis2h 0m
- 13. Mendelian Genetics4h 44m
- Introduction to Mendel's Experiments7m
- Genotype vs. Phenotype17m
- Punnett Squares13m
- Mendel's Experiments26m
- Mendel's Laws18m
- Monohybrid Crosses19m
- Test Crosses14m
- Dihybrid Crosses20m
- Punnett Square Probability26m
- Incomplete Dominance vs. Codominance20m
- Epistasis7m
- Non-Mendelian Genetics12m
- Pedigrees6m
- Autosomal Inheritance21m
- Sex-Linked Inheritance43m
- X-Inactivation9m
- 14. DNA Synthesis2h 27m
- 15. Gene Expression3h 20m
- 16. Regulation of Expression3h 31m
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression13m
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons27m
- The Lac Operon21m
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon25m
- The Trp Operon20m
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon11m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation9m
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications16m
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control22m
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation28m
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation13m
- 17. Viruses37m
- 18. Biotechnology2h 58m
- 19. Genomics17m
- 20. Development1h 5m
- 21. Evolution3h 1m
- 22. Evolution of Populations3h 53m
- 23. Speciation1h 37m
- 24. History of Life on Earth2h 6m
- 25. Phylogeny2h 31m
- 26. Prokaryotes4h 59m
- 27. Protists1h 12m
- 28. Plants1h 22m
- 29. Fungi36m
- 30. Overview of Animals34m
- 31. Invertebrates1h 2m
- 32. Vertebrates50m
- 33. Plant Anatomy1h 3m
- 34. Vascular Plant Transport1h 2m
- 35. Soil37m
- 36. Plant Reproduction47m
- 37. Plant Sensation and Response1h 9m
- 38. Animal Form and Function1h 19m
- 39. Digestive System1h 10m
- 40. Circulatory System1h 49m
- 41. Immune System1h 12m
- 42. Osmoregulation and Excretion50m
- 43. Endocrine System1h 4m
- 44. Animal Reproduction1h 2m
- 45. Nervous System1h 55m
- 46. Sensory Systems46m
- 47. Muscle Systems23m
- 48. Ecology3h 11m
- Introduction to Ecology20m
- Biogeography14m
- Earth's Climate Patterns50m
- Introduction to Terrestrial Biomes10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Near Equator13m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Temperate Regions10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Northern Regions15m
- Introduction to Aquatic Biomes27m
- Freshwater Aquatic Biomes14m
- Marine Aquatic Biomes13m
- 49. Animal Behavior28m
- 50. Population Ecology3h 41m
- Introduction to Population Ecology28m
- Population Sampling Methods23m
- Life History12m
- Population Demography17m
- Factors Limiting Population Growth14m
- Introduction to Population Growth Models22m
- Linear Population Growth6m
- Exponential Population Growth29m
- Logistic Population Growth32m
- r/K Selection10m
- The Human Population22m
- 51. Community Ecology2h 46m
- Introduction to Community Ecology2m
- Introduction to Community Interactions9m
- Community Interactions: Competition (-/-)38m
- Community Interactions: Exploitation (+/-)23m
- Community Interactions: Mutualism (+/+) & Commensalism (+/0)9m
- Community Structure35m
- Community Dynamics26m
- Geographic Impact on Communities21m
- 52. Ecosystems2h 36m
- 53. Conservation Biology24m
39. Digestive System
Digestion
Problem 9a
Textbook Question
Use the Nutrition Facts label to the right to answer these questions: What percentage of the recommended daily value of fat is found in a 1-cup serving?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the serving size on the Nutrition Facts label. In this case, it is 2/3 cup (55g).
Locate the Total Fat content per serving. Here, it is listed as 8g.
Find the % Daily Value (%DV) for Total Fat. The label indicates that 8g of Total Fat corresponds to 10% of the recommended daily value.
Determine the serving size you are interested in. The question asks for a 1-cup serving.
Calculate the percentage of the recommended daily value of fat for a 1-cup serving by adjusting the %DV proportionally from the 2/3 cup serving size.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
52sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nutrition Facts Label
The Nutrition Facts label provides essential information about the nutritional content of food products. It includes details such as serving size, calories, and the percentage of daily values (%DV) for various nutrients. Understanding this label is crucial for making informed dietary choices and managing nutrient intake.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Nutritional Diversity Among Microbes
Daily Value (%DV)
The Daily Value (%DV) indicates how much a nutrient in a serving of food contributes to a daily diet, based on a standard 2,000-calorie intake. It helps consumers understand the nutritional significance of a food item in the context of their overall diet. A %DV of 10% means that one serving provides 10% of the recommended daily intake for that nutrient.
Recommended video:
Guided course
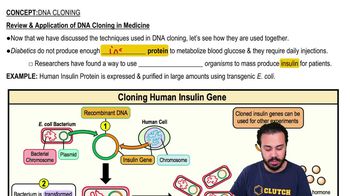
Review & Application of DNA Cloning in Medicine
Fat Content
Fat content in food is typically categorized into total fat, saturated fat, and trans fat. The total fat percentage on the Nutrition Facts label reflects how much of the daily recommended fat intake is met by one serving. Understanding fat content is important for managing health, as excessive intake can lead to various health issues, including heart disease.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Map of the Lesson on Biomolecules
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1471
views


