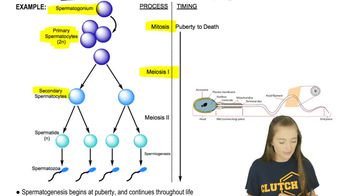
How does a zygote differ from a mature egg?
a. A zygote has more chromosomes.
b. A zygote is smaller.
c. A zygote consists of more than one cell.
d. A zygote divides by meiosis.

 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 27 Reproduction and Embryonic Development
Ch. 27 Reproduction and Embryonic Development Problem 15
Problem 15 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

How does a zygote differ from a mature egg?
a. A zygote has more chromosomes.
b. A zygote is smaller.
c. A zygote consists of more than one cell.
d. A zygote divides by meiosis.
A woman had several miscarriages. Her doctor suspected that a hormonal insufficiency was causing the lining of the uterus to break down, as it does during menstruation, terminating her pregnancies. Treatment with which of the following might help her remain pregnant?
a. Oxytocin
b. Follicle-stimulating hormone
c. Luteinizing hormone
d. Prolactin
Should parents undergoing in vitro fertilization have the right to choose which embryos to implant based on genetic criteria, such as the presence or absence of disease-causing genes? Should they be able to choose based on the sex of the embryo? How could you distinguish acceptable from unacceptable criteria? Do you think such options should be legislated?