Imagine you have found a small quantity of DNA. Fill in the following diagram, which outlines a series of DNA technology experiments you could perform to study this DNA.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Imagine you have found a small quantity of DNA. Fill in the following diagram, which outlines a series of DNA technology experiments you could perform to study this DNA.
<IMAGE>
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Which of the following would be considered a transgenic organism?
a. A bacterium that has received genes via conjugation
b. A human given a corrected human blood-clotting gene
c. A fern grown in cell culture from a single fern root cell
d. A rat with rabbit hemoglobin genes
A paleontologist has recovered a tiny bit of organic material from the 400-year-old preserved skin of an extinct dodo. She would like to compare DNA from the sample with DNA from living birds. Which of the following would be most useful for increasing the amount of DNA available for testing?
a. Restriction fragment analysis
b. Polymerase chain reaction
c. Molecular probe analysis
d. Electrophoresis
How many genes are there in a human sperm cell?
a. 23
b. 46
c. About 21,000
d. about 3 billion
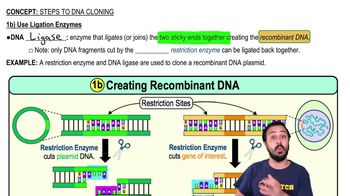
When a typical restriction enzyme cuts a DNA molecule, the cuts are uneven, giving the DNA fragments single-stranded ends. These ends are useful in recombinant DNA work because
a. They enable a cell to recognize fragments produced by the enzyme.
b. They serve as starting points for DNA replication.
c. The fragments will bond to other fragments with complementary ends.
d. They enable researchers to use the fragments as molecular probes.