If a base-pair change occurs in DNA, this a. is a mutation. b. would be a mutation only if it falls in a protein-coding part of a gene. c. would be a mutation only if it falls in a transcribed part of the genome. d. is not a mutation, because only one base pair has been altered.
Ch. 16 - How Genes Work

Chapter 16, Problem 1
What does a bacterial RNA polymerase produce when it transcribes a protein-coding gene?a. rRNAb. tRNAc. mRNAd. snRNA
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the function of RNA polymerase in bacteria, which is to synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Understand the different types of RNA that can be produced: rRNA (ribosomal RNA), tRNA (transfer RNA), mRNA (messenger RNA), and snRNA (small nuclear RNA).
Recognize that the question specifically asks about the transcription of a protein-coding gene.
Recall that mRNA is the type of RNA that carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where proteins are synthesized.
Conclude that the RNA polymerase produces mRNA when it transcribes a protein-coding gene.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which RNA is synthesized from a DNA template. In this process, RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of the DNA and unwinds the double helix, allowing it to read the gene's coding sequence. The result of transcription is the formation of a complementary RNA strand, which can then be processed and translated into a protein.
Recommended video:
Guided course

1) Initiation of Transcription
Types of RNA
There are several types of RNA produced in cells, each serving distinct functions. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis, while transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) play roles in translating that information into proteins. Understanding these types is crucial for grasping how genes are expressed and proteins are made.
Recommended video:
Guided course
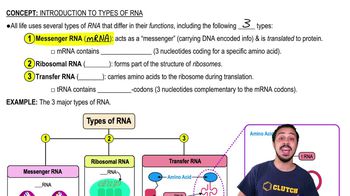
Introduction to Types of RNA
Bacterial RNA Polymerase
Bacterial RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA from a DNA template in prokaryotic cells. Unlike eukaryotic cells, bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that transcribes all types of RNA, including mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. This enzyme initiates transcription at specific promoter regions and is essential for gene expression in bacteria.
Recommended video:
Guided course

DNA Polymerase Requirements
Related Practice
Textbook Question
856
views
Textbook Question
If a base-pair change occurs in DNA, thisa. is a mutation.b. would be a mutation only if it falls in a protein-coding part of a gene.c. would be a mutation only if it falls in a transcribed part of the genome.d. is not a mutation, because only one base pair has been altered.
845
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following is an important exception to the central dogma of molecular biology?
a. Many genes code for RNAs that function directly in the cell.
b. DNA is the repository of genetic information in all cells.
c. Messenger RNA is a short-lived 'information carrier.
d. Proteins are responsible for most aspects of the phenotype.
2512
views
Textbook Question
DNA's primary structure is made up of just four different bases, and its secondary structure is regular and highly stable. How can a molecule with these characteristics hold the information required to build and maintain a cell?
1266
views
