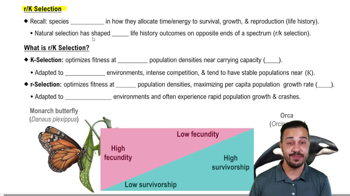
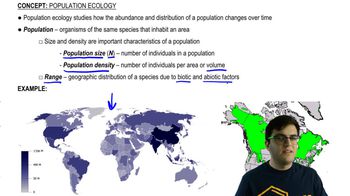
A population's carrying capacity
a. May change as environmental conditions change
b. Can be accurately calculated using the logistic growth model
c. Increases as the per capita population growth rate decreases
d. Can never be exceeded
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: