The possibility of extensive genetic testing raises questions about how personal genetic information should be used. Might some people avoid being tested for fear of being labeled genetic outcasts?

Scientists investigate hypotheses using a variety of methods, depending on the circumstances behind the research. Human nutrition studies (such as those studying whether GMO foods have any health effects) are particularly problematic. Can you design a hypothetical human nutrition study to test whether GMO corn is less healthy than traditional corn? Can you identify real-world problems that may interfere with your design and confound your results?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Hypothesis Testing
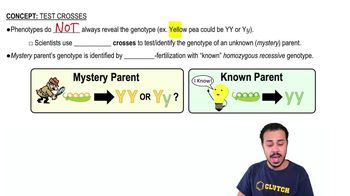
Confounding Variables

Study Design

The possibility of extensive genetic testing raises questions about how personal genetic information should be used. Or might they be compelled to be tested against their wishes? Can you think of other reasons to proceed with caution?
The possibility of extensive genetic testing raises questions about how personal genetic information should be used.
The fruits of wild species of tomato are tiny compared with the giant beefsteak tomatoes available today. This difference in fruit size is almost entirely due to the larger number of cells in the domesticated fruits. Plant biologists have recently discovered genes that are responsible for controlling cell division in tomatoes.
Why would such a discovery be important to producers of other kinds of fruits and vegetables?
To the study of human development and disease?
To our basic understanding of biology?
