Textbook Question
After S phase, what makes up a single chromosome?
a. Two daughter chromosomes
b. A double-stranded DNA molecule
c. Two single-stranded DNA molecules
d. Two sister chromatids
2418
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


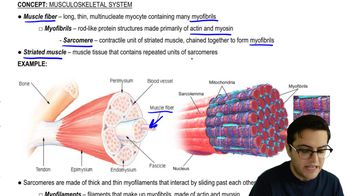
After S phase, what makes up a single chromosome?
a. Two daughter chromosomes
b. A double-stranded DNA molecule
c. Two single-stranded DNA molecules
d. Two sister chromatids
Progression through the cell cycle is regulated by oscillations in the concentration of which type of molecule?
a. p53, Rb, and other tumor suppressors
b. Receptor tyrosine kinases
c. Cyclins
d. Cyclin-dependent kinases
What major events occur during anaphase of mitosis?