In flies, small wings are recessive to normal wings. If a cross between two flies produces 8 small-wing offspring and 28 normal-wing offspring, what are the most likely genotypes of the parents? (Use S to represent the normal-wing allele and s to represent the short-wing allele.)

In garden peas, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y), and inflated pods (I) are dominant to constricted pods (i). Suppose you have crossed YYII parents with yyii parents. Draw the F2 Punnett square. Based on this Punnett square, predict the expected phenotype(s) in the F2 generation and the expected frequency of each phenotype.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Mendelian Genetics

Punnett Square

Phenotypic Ratios
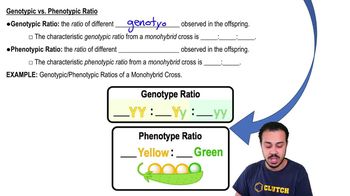
In garden peas, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y), and inflated pods (I) are dominant to constricted pods (i). Suppose you have crossed YYII parents with yyii parents. Draw the F1 Punnett square and predict the expected F1 phenotype(s).
In garden peas, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y), and inflated pods (I) are dominant to constricted pods (i). Suppose you have crossed YYII parents with yyii parents. List the genotype(s) of gametes produced by F1 individuals.
In garden peas, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y), and inflated pods (I) are dominant to constricted pods (i). Suppose you have crossed YYII parents with yyii parents. Draw the F2 Punnett square. Based on this Punnett square, predict the expected phenotype(s) in the F2 generation and the expected frequency of each phenotype.
