Textbook Question
Activators bind to regulatory sequences in ________ and to ________ polymerase.
1205
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


A regulon is a set of genes controlled by
a. One type of regulator of transcription
b. Two or more different alternative sigma proteins
c. Many different types of promoters
d. Glucose
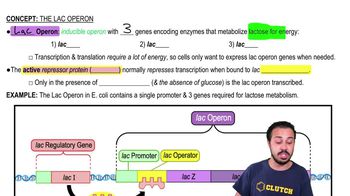
Predict what would happen to regulation of the lac operon if the lacI gene were moved 50,000 nucleotides upstream of its normal location.