Textbook Question
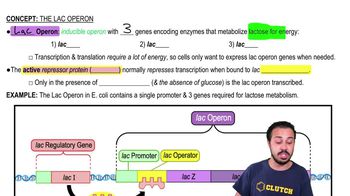
Why are the genes involved in lactose metabolism considered to be an operon?a. They occupy adjacent locations on the E. coli chromosome.b. They have a similar function.c. They are all required for normal cell function.d. They are all controlled by the same promoter.
912
views