- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A researcher collects a random sample of delivery times (in minutes) for a food service. The sample has a mean of , and it is known that the population standard deviation is minutes. The company claims that the average delivery time is minutes. Under what conditions can you use a -test to test whether the population mean is minutes?
A technician monitors the daily performance of a machine and records whether it passes or fails quality checks over consecutive days. The outcomes are shown as a sequence of (pass) and (fail):
The technician claims that the pattern is not random. State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses.
Determine the critical value and rejection region for a right-tailed -test with and .
For a two-tailed hypothesis test, the standardized test statistic is and the significance level is . What is the -value, and do you reject ?
A market analyst is testing whether product preference (Product A, B, or C) is independent of customer age group (under , , over ). She surveys customers and constructs a contingency table.
At the significance level, what is the critical chi-square value? What is the rejection region?
A company tests a productivity tool on employees by recording their productivity (in tasks/hour) before and after using the tool. Using the sign test, they obtain a test statistic of based on non-zero differences. At the significance level, the critical value is . Should the company reject the null hypothesis? What can be concluded about the tool’s effectiveness?
A researcher collects data on reaction times (in units of milliseconds) from drivers using four different types of dashboard displays. The goal is to test whether the mean reaction times are the same for all display types. The researcher uses ANOVA for the analysis. Why is this method called "analysis of variance" when the objective is to compare means?
A nutritionist wants to compare the effects of two different diets on weight loss. After weeks, the following statistics are recorded:
Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Use degrees of freedom equal to the smaller of and . Construct a confidence interval for the difference in mean weight loss, where the difference is defined as the mean for the Diet X group minus the mean for the Diet Y group.
A researcher suspects that coin flips from a vending machine are not fair. In flips, there are only heads. Use a two-tailed binomial test with . Let , , and use binomial critical values. What are the critical values for this test?
A courier company claims that the median delivery time for local packages is minutes. In a random sample of deliveries, the recorded times (in minutes) were:
i) Identify the claim and state and .
ii) At the significance level, can you reject the company’s claim? Interpret the decision.
A factory manager claims that the average daily output of machines is greater than units. To test this claim, a random sample of machines shows a mean output of units per day. The population standard deviation is known to be units. At the level of significance, is there sufficient evidence to support the manager’s claim?
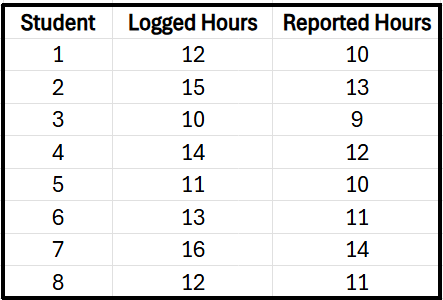
Listed below are the actual study hours logged by students and the study hours those same students reported in a survey. Assume the samples are simple random samples and the differences have an approximately normal distribution.
Use a significance level to test the claim that the actual study hours logged by students are higher than their reported study hours.
A food safety agency states that no more than of all packaged chicken breasts sold in major grocery stores contain trace amounts of a certain pathogen. A researcher, believing the true rate is higher, tests randomly selected packages. Which of the following correctly states the null and alternative hypotheses for the researcher's test?
The following are the numbers of annual tornado-related fatalities in a certain country over consecutive years: . Additionally, in a recent study, there were tornado fatalities among adults and among children. Assume these are random samples and test the claim that the proportion of adult fatalities is greater than at the significance level. What might explain the result?
A large electronics company claims that the defect rate for its flagship smartphone model is or less after the first year of use. A consumer advocacy group suspects the actual defect rate is different from . The group surveys a random sample of owners who have had the phone for over a year. Of these owners, reported experiencing a major hardware defect. Determine the -value for a two-tailed hypothesis test to check if the true proportion of defective phones is significantly different from .