- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Why is a prediction interval generally wider than a confidence interval for the mean response?
A mechanic is studying the relationship between the weight of a car (, in hundreds of pounds) and its fuel efficiency (, in ). The data collected is shown below:
Predict the fuel efficiency () for a car that weighs hundred pounds. Consider .
Given x values: 2, 4, 6, 8, what is x̄ and Σx²?
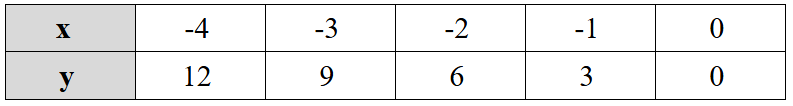
Consider the relationship between and provided in the table below:
Predict the value of when .
Given t = 2.228, s = 40, n = 8, x₀ = 10, x̄ = 8, Σx = 64, Σx² = 704, calculate the margin of error for the prediction interval at x₀ = 10. Use the formula:E = t * s * sqrt[1 + 1/n + (x₀ - x̄)² / (n*Σx² - (Σx)²)]
If a prediction interval is very wide, what does this suggest about the regression model or data?
Researchers analyzed the relationship between the average price of a used car (in units of thousands of dollars) and the average price of a new car (in units of thousands of dollars) over years. The regression equation is , with , , , and . Find the prediction interval for the average used car price when the new car price is . (Use ).
How does a prediction interval differ from a confidence interval in regression analysis?
A study examined the relationship between tire width (in units of millimeters) and braking distance (in units of meters) for a set of sports cars. For a tire width of millimeters, the statistical software output produces a percent prediction interval for braking distance as to meters. What is the prediction interval estimate for braking distance for a car with -millimeter-wide tires, and what does this interval mean?
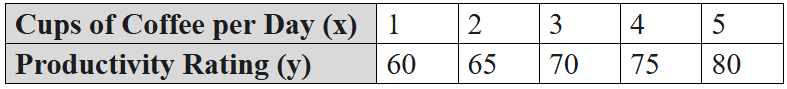
A small business owner suspects a link between employees' daily coffee consumption and their daily productivity rating.
Predict the mean productivity rating for all employees who drink cups of coffee per day.