17–22. Position from velocity Consider an object moving along a line with the given velocity v and initial position.
a. Determine the position function, for t≥0, using the antiderivative method
v(t) = −t³+3t²−2t on [0, 3]; s(0)=4
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: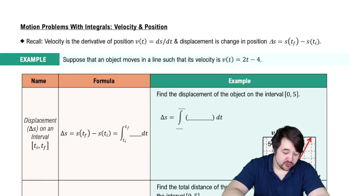


 1:17m
1:17mMaster Using The Velocity Function with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning