Graph each equation in a rectangular coordinate system. 3x -18=0
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Lines
Problem 2
Textbook Question
Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence. The graph of the line y= -2x+7 has slope ______ and y-intercept ______.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
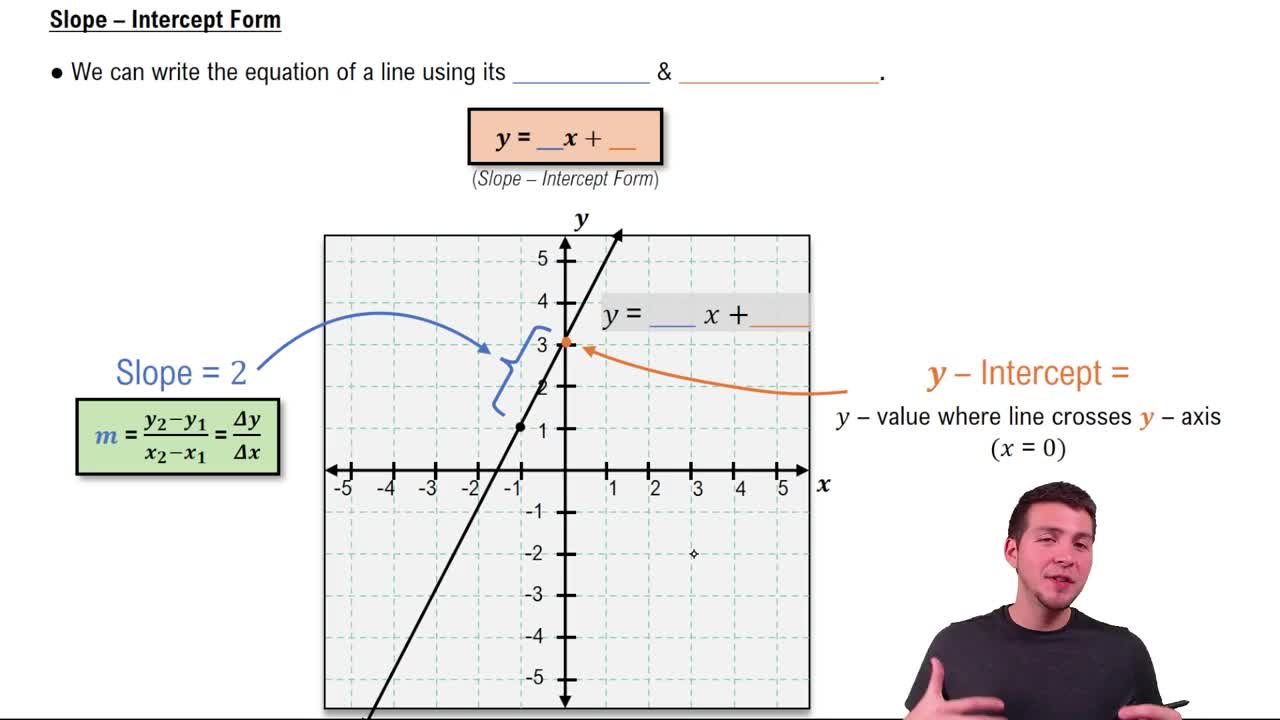
Identify the slope-intercept form of a linear equation, which is given by \(y = mx + b\), where \(m\) represents the slope and \(b\) represents the y-intercept.
Compare the given equation \(y = -2x + 7\) to the slope-intercept form to determine the values of \(m\) and \(b\).
From the equation, observe that the coefficient of \(x\) is \(-2\), so the slope \(m\) is \(-2\).
Also, the constant term is \$7\(, which means the y-intercept \)b\( is \)7$.
Therefore, the slope is \(-2\) and the y-intercept is \$7$.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Slope of a Line
The slope of a line measures its steepness and direction, represented by the coefficient of x in the equation y = mx + b. It indicates how much y changes for a unit change in x. A negative slope means the line decreases as x increases.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Slope of a Line
Y-Intercept of a Line
The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis, given by the constant term b in the equation y = mx + b. It represents the value of y when x is zero, providing a starting point for graphing the line.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphing Lines in Slope-Intercept Form
Slope-Intercept Form of a Linear Equation
The slope-intercept form y = mx + b expresses a linear equation clearly showing the slope (m) and y-intercept (b). This form makes it easy to identify key features of the line and to graph it quickly.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Slope-Intercept Form
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
490
views


