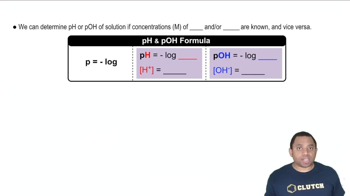
Textbook Question
Calculate [H+] for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) [OH-] = 0.00045 M (b) [OH-] = 8.8 × 10-9 M (c) a solution in which [OH-] is 100 times greater than [H+].
375
views