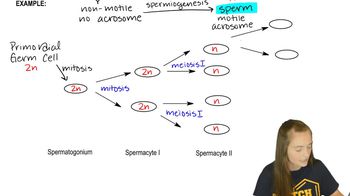
Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
Some pre-mRNA is not synthesized.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: