Two mothers give birth to sons at the same time at a busy urban hospital. The son of mother 1 is afflicted with hemophilia, a disease caused by an X-linked recessive allele. Neither parent has the disease. Mother 2 has a normal son, despite the fact that the father has hemophilia. Several years later, couple 1 sues the hospital, claiming that these two newborns were swapped in the nursery following their birth. As a genetic counselor, you are called to testify. What information can you provide the jury concerning the allegation?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Pedigrees
Problem 40
Textbook Question
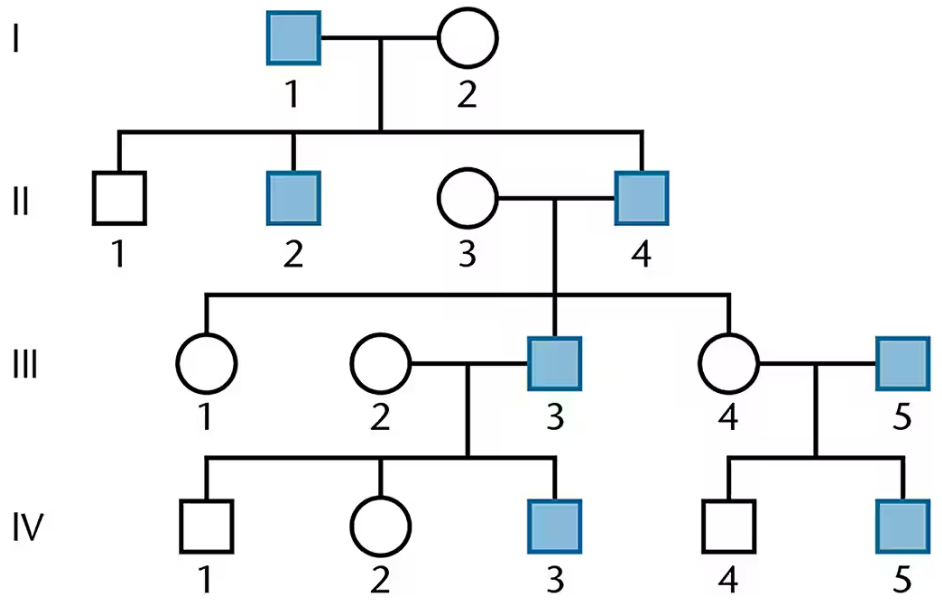
The following pedigree is characteristic of an inherited condition known as male precocious puberty, where affected males show signs of puberty by age 4. Propose a genetic explanation of this phenotype.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Analyze the pedigree to determine the inheritance pattern. Look for clues such as whether the condition is passed from father to son, whether females are affected, and whether the condition skips generations. This will help identify if the trait is autosomal or sex-linked, and dominant or recessive.
Consider the phenotype described in the problem: male precocious puberty. Since the condition specifically affects males, this suggests the possibility of a sex-linked inheritance pattern, likely X-linked or Y-linked.
Evaluate whether the condition could be Y-linked. If the condition is Y-linked, it would only affect males and would be passed directly from father to son without skipping generations. Check the pedigree for this pattern.
If the condition does not fit a Y-linked pattern, consider the possibility of an autosomal dominant inheritance with sex-limited expression. In this case, the gene could be present in both males and females, but the phenotype is only expressed in males due to hormonal or developmental factors.
Propose a genetic explanation based on the evidence. For example, if the condition is Y-linked, it could be caused by a mutation in a gene on the Y chromosome that regulates male puberty. If it is autosomal dominant with sex-limited expression, it could involve a mutation in a gene that interacts with male-specific hormones or pathways.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is a diagrammatic method used to trace the inheritance patterns of traits through generations in a family. It helps identify whether a trait is autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked by examining the affected individuals and their relatives. Understanding how traits are passed down is crucial for proposing genetic explanations for conditions like male precocious puberty.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Pedigree Flowchart
Genetic Inheritance Patterns
Genetic inheritance patterns describe how traits and conditions are transmitted from parents to offspring. In the case of male precocious puberty, it is important to consider whether the condition is linked to a specific gene mutation, and whether it follows a dominant or recessive inheritance pattern. This understanding aids in predicting the likelihood of occurrence in future generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Diploid Genetics
Hormonal Regulation and Genetic Mutations
Hormonal regulation involves the control of bodily functions through hormones, which can be influenced by genetic mutations. In male precocious puberty, mutations in genes that regulate hormone production or signaling pathways can lead to early onset of puberty. Identifying these mutations is essential for understanding the genetic basis of the phenotype and its implications for affected individuals.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Regulation
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
445
views


