Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Branched Pathways in Metabolism
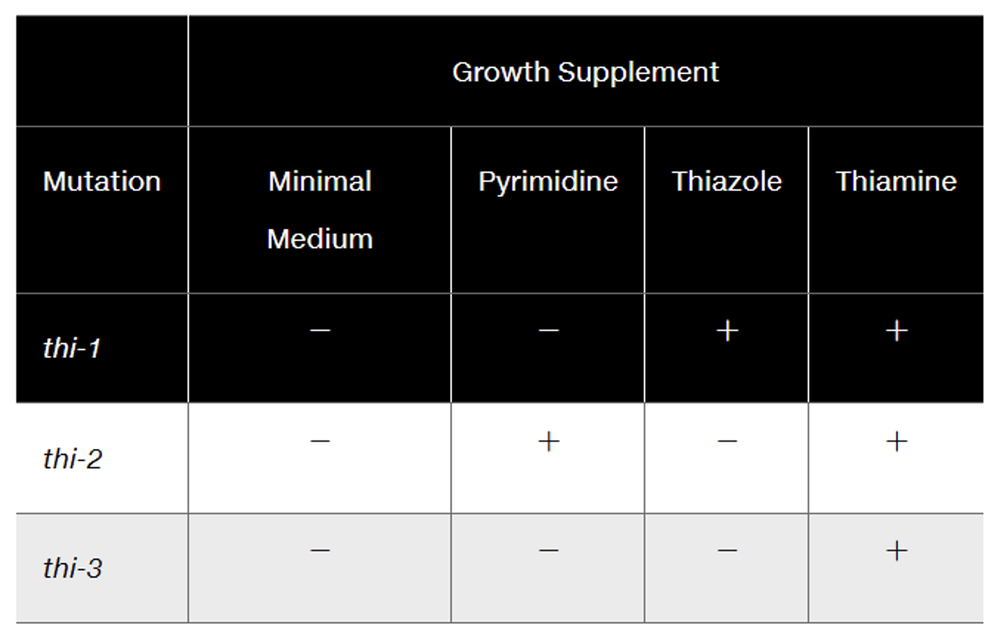
Branched pathways in metabolism refer to biochemical routes where a single precursor can lead to multiple end products through various enzymatic reactions. In the context of thiamine synthesis, this means that different mutations can affect different branches of the pathway, leading to distinct outcomes in growth depending on the available supplements.
Recommended video:
Mutations and Their Effects
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can alter the function of genes, often affecting enzyme production in metabolic pathways. In the case of Neurospora, the mutations (thi-1, thi-2, thi-3) demonstrate how specific genetic changes can disrupt thiamine synthesis, revealing the complexity of metabolic regulation and the necessity of certain intermediates for growth.
Recommended video:
Supplementation and Growth Conditions
Supplementation refers to the addition of specific nutrients to a growth medium to support the development of organisms. The data indicates that certain mutants can grow in the presence of specific supplements (like pyrimidine or thiazole), suggesting that these compounds are intermediates in the thiamine synthesis pathway, further supporting the idea of a branched rather than a linear pathway.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

