Because the degree of DNA methylation appears to be a relatively reliable genetic marker for some forms of cancer, researchers have explored the possibility of altering DNA methylation as a form of cancer therapy. Initial studies indicate that while hypomethylation suppresses the formation of some tumors, other tumors thrive. Why would one expect different cancers to respond differently to either hypomethylation or hypermethylation therapies?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Epigenetics, Chromatin Modifications, and Regulation
Problem 22b
Textbook Question
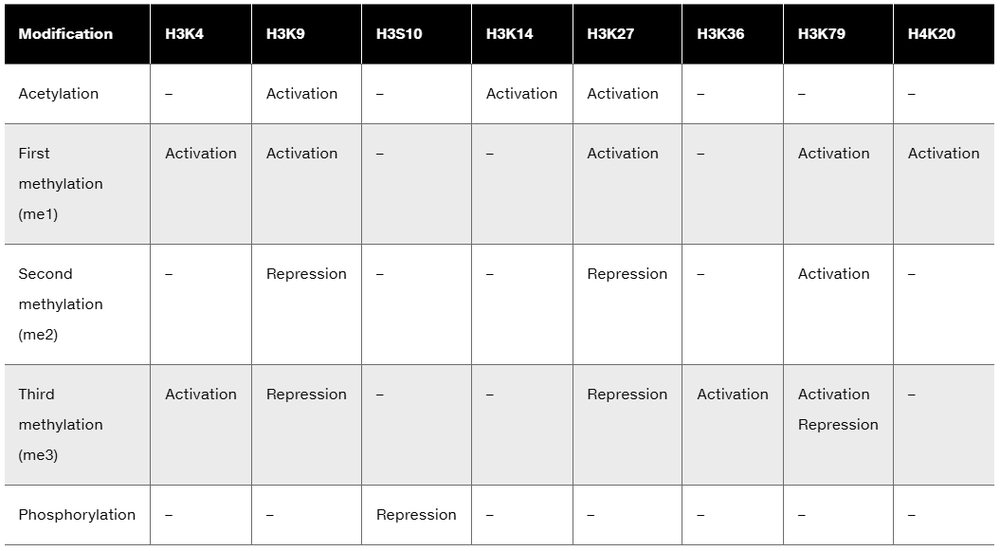
From the following table, draw up a list of histone H3 modifications associated with gene activation. Then draw up a list of H3 modifications associated with repression.
Are these overlaps explained by different modifications?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand that histone H3 modifications are chemical changes to the histone protein that affect chromatin structure and gene expression. Common modifications include methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination, each occurring at specific amino acid residues on histone H3.
Step 2: Compile a list of histone H3 modifications associated with gene activation. These typically include acetylation at lysine residues such as H3K9ac (acetylation at lysine 9) and H3K27ac, as well as methylation marks like H3K4me3 (trimethylation at lysine 4), which are known to correlate with active transcription.
Step 3: Compile a list of histone H3 modifications associated with gene repression. These often include methylation marks such as H3K9me3 and H3K27me3, which are linked to heterochromatin formation and transcriptional silencing.
Step 4: Analyze whether there is overlap between activating and repressing modifications. Consider that some residues can be modified in different ways (e.g., methylation vs. acetylation) leading to different functional outcomes, and that the same residue can carry different modifications in different contexts.
Step 5: Conclude that the overlaps in histone H3 modifications are explained by the fact that different types of chemical modifications at the same or different residues can have distinct effects on gene expression, highlighting the complexity and combinatorial nature of the histone code.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Histone H3 Modifications and Their Role in Gene Regulation
Histone H3 undergoes various post-translational modifications, such as methylation and acetylation, which influence chromatin structure and gene expression. Specific modifications can either promote gene activation by loosening chromatin or cause repression by tightening it, thus controlling access to DNA.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Histone Protein Modifications
Histone Code Hypothesis and Modification Specificity
The histone code hypothesis suggests that distinct combinations of histone modifications create a regulatory language that determines gene activity. Different modifications on histone H3, like methylation at different lysine residues, can have opposing effects, explaining how overlapping modifications can lead to activation or repression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Histone Protein Modifications
Functional Overlap and Context-Dependence of Histone Modifications
Some histone H3 modifications may appear in both active and repressed genes, but their effects depend on the specific residue modified, the type of modification, and the presence of other marks. This context-dependence allows for complex regulation and explains overlaps in modification patterns.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Histone Protein Modifications
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
518
views


