Specialized transduction differs from generalized transduction because specialized transduction is defined by what?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Transduction
Problem 20
Textbook Question
A triple-auxotrophic strain of E. coli having the genotype phe⁻ met⁻ ara⁻ is used as a recipient strain in a transduction experiment. The strain is unable to synthesize its own phenylalanine or methionine, and it carries a mutation that leaves it unable to utilize the sugar arabinose for growth. The recipient is crossed to a prototrophic strain with the genotype phe⁺ met⁺ ara⁺. The table below shows the selected marker and gives cotransduction frequencies for the unselected markers.
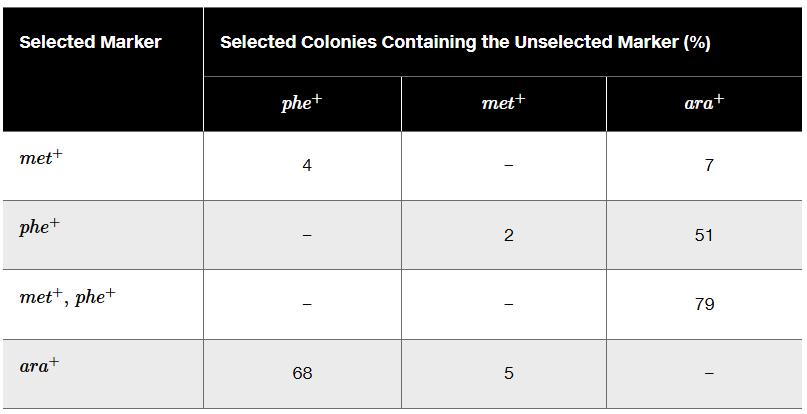
Use the cotransduction data to determine the order of these genes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by understanding the concept of cotransduction. Cotransduction occurs when two or more genes are transferred together during transduction, and the frequency of cotransduction is inversely proportional to the distance between the genes. Genes that are closer together are more likely to be cotransduced.
Examine the table provided. The table shows the cotransduction frequencies for unselected markers when a specific marker is selected. Higher cotransduction frequencies indicate that the genes are closer together.
Analyze the data for each selected marker. For example, when phe⁺ is selected, the cotransduction frequency with met⁺ is 2%, and with ara⁺ is 51%. This suggests that phe⁺ is closer to ara⁺ than to met⁺.
Similarly, when met⁺ is selected, the cotransduction frequency with phe⁺ is 4%, and with ara⁺ is 7%. This suggests that met⁺ is closer to phe⁺ than to ara⁺.
Combine the information to determine the gene order. Based on the cotransduction frequencies, the gene order is likely ara⁺ - phe⁺ - met⁺, as ara⁺ and phe⁺ have the highest cotransduction frequency, indicating they are closest, while met⁺ is farther away.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transduction
Transduction is a process of genetic transfer in bacteria where bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) carry DNA from one bacterium to another. This mechanism can lead to genetic recombination and the introduction of new traits, such as antibiotic resistance or metabolic capabilities. Understanding transduction is crucial for analyzing how genes are transferred and how they can be mapped based on cotransduction frequencies.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Transduction
Cotransduction Frequency
Cotransduction frequency refers to the likelihood that two genes will be transferred together during the transduction process. This frequency is influenced by the physical proximity of the genes on the bacterial chromosome; genes that are closer together are more likely to be cotransduced. By analyzing these frequencies, researchers can infer the relative positions of genes on a chromosome, which is essential for determining gene order.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Transduction
Genetic Mapping
Genetic mapping is the process of determining the arrangement of genes on a chromosome. It involves using data from experiments, such as cotransduction frequencies, to establish the order and distance between genes. This information is vital for understanding gene interactions, functions, and the overall genetic architecture of an organism, particularly in studies involving mutations and genetic engineering.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mapping Overview
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
776
views
1
rank


