What roles do restriction enzymes, vectors, and host cells play in recombinant DNA studies? What role does DNA ligase perform in a DNA cloning experiment? How does the action of DNA ligase differ from the function of restriction enzymes?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
18. Molecular Genetic Tools
Genetic Cloning
Problem 4a
Textbook Question
One of the major causes of sickness, death, and economic loss in the cattle industry is Mannheimia haemolytica, which causes bovine pasteurellosis, or shipping fever. Noninvasive delivery of a vaccine using transgenic plants expressing immunogens would reduce labor costs and trauma to livestock. An early step toward developing an edible vaccine is to determine whether an injected version of an antigen (usually a derivative of the pathogen) is capable of stimulating the development of antibodies in a test organism. The following table assesses the ability of a transgenic portion of a toxin (Lkt) of M. haemolytica to stimulate development of specific antibodies in rabbits.
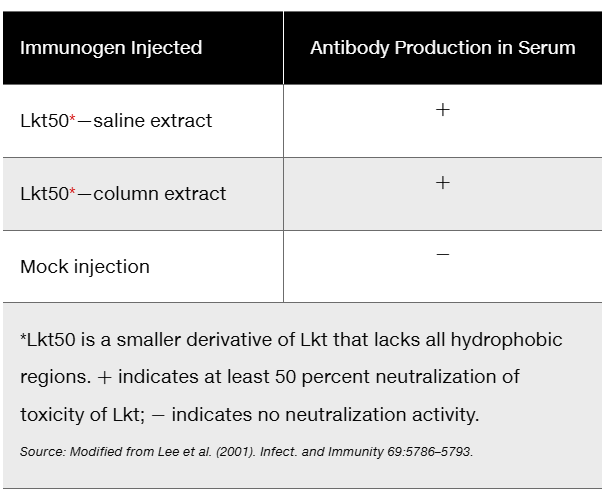
What general conclusion can you draw from the data?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Begin by analyzing the table provided in the problem. The table compares antibody production in rabbits after injection with different forms of the immunogen (Lkt50) and a mock injection. Note the '+' and '-' symbols indicating the presence or absence of antibody production.
Step 2: Understand the significance of Lkt50. It is a smaller derivative of the toxin Lkt from Mannheimia haemolytica, modified to lack hydrophobic regions, and is capable of neutralizing at least 50% of the toxicity of Lkt. This modification makes it a candidate for testing as an immunogen.
Step 3: Compare the results of the injections. Both the saline extract and column extract of Lkt50 stimulate antibody production (indicated by '+'), while the mock injection does not (indicated by '-'). This suggests that the Lkt50 derivative is immunogenic and capable of eliciting an immune response.
Step 4: Consider the implications of the data. The ability of Lkt50 to stimulate antibody production in rabbits supports its potential as a component of an edible vaccine. This is an important step in developing a noninvasive vaccine delivery system using transgenic plants.
Step 5: Formulate the general conclusion. The data indicates that the transgenic portion of the toxin (Lkt50) is effective in stimulating the development of specific antibodies in rabbits, which is a promising result for vaccine development against bovine pasteurellosis.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Antibody Production
Antibody production is a crucial aspect of the immune response, where the body generates specific proteins (antibodies) to identify and neutralize pathogens. In the context of vaccines, the goal is to stimulate this response through the introduction of antigens, which are components of the pathogen. The effectiveness of an antigen in eliciting an antibody response can be assessed by measuring the levels of antibodies in the serum after immunization.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Proteomics
Transgenic Plants
Transgenic plants are genetically modified organisms that have had foreign genes inserted into their genome. This technology allows for the expression of specific proteins, such as immunogens from pathogens, in plant tissues. The use of transgenic plants for vaccine production offers a non-invasive method to deliver vaccines, potentially reducing costs and improving animal welfare by eliminating the need for injections.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Plant Gamete Terminology
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity refers to the ability of a substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response. In vaccine development, it is essential to determine whether a particular antigen can stimulate the production of antibodies. The data presented in the question indicates that the Lkt50 extracts are capable of inducing antibody production, suggesting their potential as effective immunogens in vaccine formulations against Mannheimia haemolytica.
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
692
views


