What is a plasmid?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Working with Microorganisms
Problem 1a
Textbook Question
How do we know that genes exist in bacteria and bacteriophages?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the historical context: Scientists first observed that bacteria and bacteriophages exhibit heritable traits, such as antibiotic resistance in bacteria or the ability of bacteriophages to infect specific bacterial strains. This suggested the presence of genetic material controlling these traits.
Review experiments demonstrating transformation: Frederick Griffith's experiments with Streptococcus pneumoniae showed that non-virulent bacteria could acquire virulence from heat-killed virulent bacteria. This transformation indicated the presence of genetic material in bacteria.
Examine experiments on conjugation: Joshua Lederberg and Edward Tatum demonstrated bacterial conjugation, where genetic material is transferred between bacterial cells through direct contact. This provided further evidence of genes in bacteria.
Consider bacteriophage experiments: The Hershey-Chase experiment used radioactive labeling to show that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material transferred by bacteriophages into bacteria during infection. This confirmed the existence of genes in bacteriophages.
Analyze genetic mapping techniques: Techniques such as interrupted mating experiments in bacteria and recombination frequency analysis in bacteriophages allowed scientists to map genes, further proving their existence and organization in these organisms.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gene Theory
Gene theory posits that genes are the fundamental units of heredity, responsible for the transmission of traits from one generation to the next. In bacteria and bacteriophages, genes are segments of DNA that encode proteins, influencing various biological functions. The existence of genes in these organisms is supported by experimental evidence, such as mutations and phenotypic changes that correlate with specific genetic alterations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping Genes
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination is a process by which genetic material is exchanged between organisms, leading to new combinations of genes. In bacteria, this can occur through mechanisms like transformation, transduction, and conjugation, while bacteriophages can introduce new genetic material into bacterial genomes. This process not only demonstrates the presence of genes but also allows geneticists to map and study the genetic structure of these organisms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
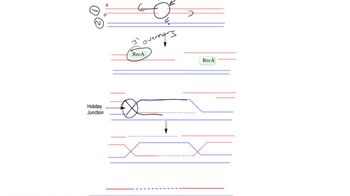
Recombination after Double Strand Breaks
Molecular Techniques
Molecular techniques, such as DNA sequencing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR), are essential tools for identifying and studying genes in bacteria and bacteriophages. These methods enable scientists to analyze genetic material directly, providing evidence for the existence of specific genes and their functions. By employing these techniques, researchers can confirm the presence of genes and explore their roles in various biological processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping with Markers

 9:35m
9:35mWatch next
Master Bacteria in the Laboratory with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
615
views
2
rank
