How do the ENCODE data vastly help determine which enhancers regulate which genes?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
10. Transcription
Transcription in Eukaryotes
Problem 25a
Textbook Question
The accompanying illustration shows a portion of a gene undergoing transcription. The template and coding strands for the gene are labeled, and a segment of DNA sequence is given.
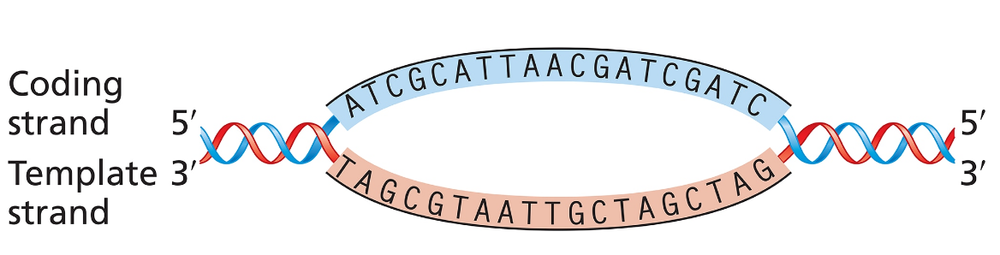
For this gene segment, superimpose a drawing of RNA polymerase as it nears the end of transcription of the DNA sequence.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the process of transcription: Transcription is the process by which RNA polymerase synthesizes a complementary RNA strand from the DNA template strand. The RNA sequence will be complementary to the template strand and identical (except for uracil replacing thymine) to the coding strand.
Identify the direction of transcription: RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, synthesizing the RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction. Ensure you know which end of the DNA sequence corresponds to 3' and 5'.
Locate the RNA polymerase position: Since the problem states that RNA polymerase is nearing the end of transcription, it should be positioned close to the 5' end of the template strand (or the 3' end of the coding strand).
Superimpose the RNA polymerase: Draw the RNA polymerase as a large enzyme complex near the end of the template strand. Ensure that the RNA strand being synthesized is shown emerging from the RNA polymerase in the 5' to 3' direction.
Label the components: Clearly label the template strand, coding strand, RNA polymerase, and the RNA strand being synthesized. This will help clarify the relationships between the DNA and RNA during transcription.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). During this process, RNA polymerase binds to the DNA template strand and synthesizes a complementary RNA strand. This occurs in three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination, with RNA polymerase playing a crucial role in catalyzing the formation of RNA from the DNA template.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transcription
RNA Polymerase
RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA from a DNA template during transcription. It unwinds the DNA double helix and adds ribonucleotides to the growing RNA strand in a 5' to 3' direction. The enzyme also recognizes specific promoter regions on the DNA to initiate transcription and is involved in terminating the process once a termination signal is reached.
Recommended video:
Gene Structure
A gene consists of sequences of DNA that encode instructions for synthesizing proteins. It typically includes regulatory regions, exons (coding sequences), and introns (non-coding sequences). Understanding the structure of a gene is essential for comprehending how transcription occurs, as it determines where RNA polymerase binds and how the resulting mRNA is processed before translation into proteins.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ribosome Structure

 9:16m
9:16mWatch next
Master Eukaryotic Transcription with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
564
views

